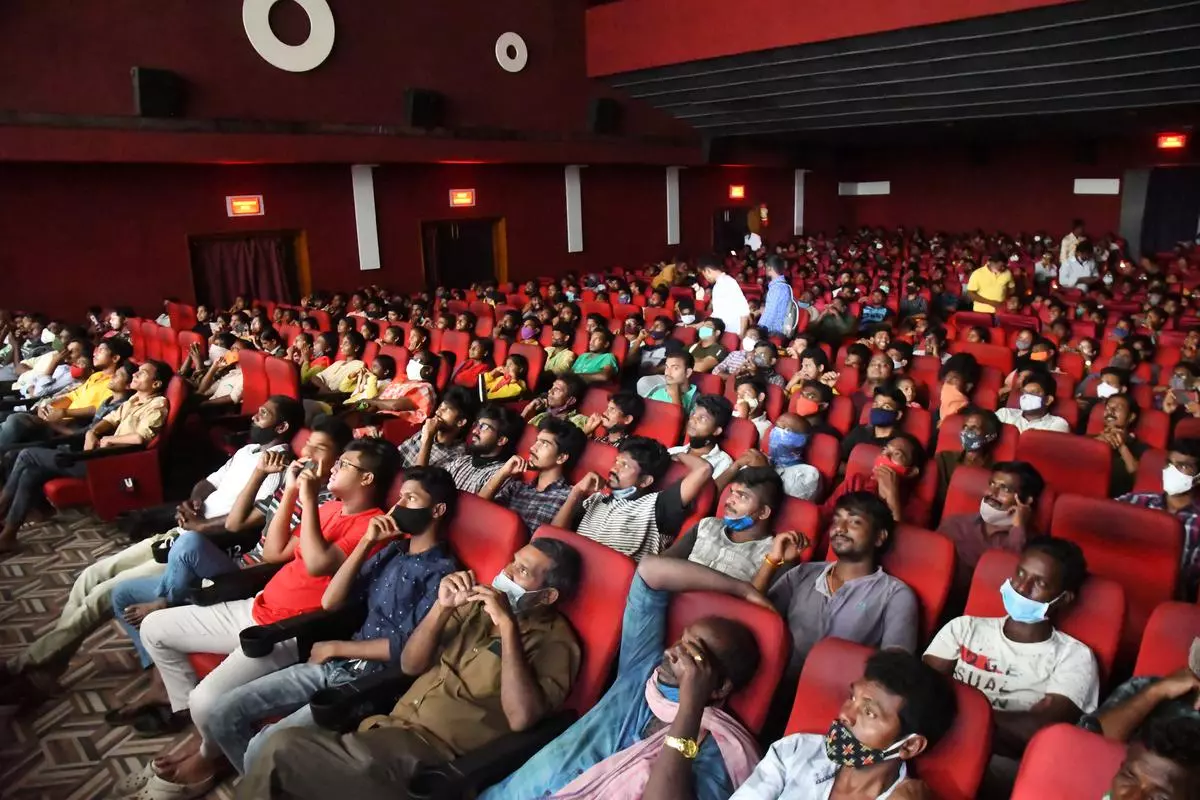
In 2023, India witnessed a modest increase in the number of movie screens, with Hindi-speaking regions leading the growth, followed by the east and south, as per the latest FICCI-EY media and entertainment industry report. Despite the pandemic-induced challenges, the country’s cinema landscape showed signs of recovery, with the total number of screens surpassing 2018 levels. However, the expansion remains heavily skewed towards certain regions like Delhi NCR, Maharashtra, and Bengaluru, leaving states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Odisha relatively underserved. High real estate costs and audience disconnect with contemporary movie themes contribute to this imbalance. Multiplex chains are eyeing expansion into untapped markets, awaiting infrastructure development for further growth.
India’s cinema industry, renowned globally for its diverse and vibrant film culture, has faced various challenges in recent years. The COVID-19 pandemic dealt a severe blow to the sector, forcing many theatres to shut down temporarily or permanently. The subsequent restrictions on movie releases and audience capacity further exacerbated the situation. Despite these setbacks, the gradual reopening of theatres and the resurgence of audience interest in cinematic experiences have injected a sense of optimism into the industry.
The increase in the number of movie screens in 2023, albeit modest, reflects a positive trend amidst adversity. The growth, particularly in Hindi-speaking markets, underscores the resilience of regional film industries and their ability to adapt to changing circumstances. The rise in screens in the east and south also signifies the importance of these regions in the overall cinematic landscape of the country.
However, the disparity in screen distribution across different states remains a notable challenge. While states like Maharashtra and Karnataka boast a significant number of screens, others such as Bihar and Jharkhand lag behind. This imbalance not only limits access to cinema for residents of these regions but also hampers the growth potential of the industry as a whole.
One of the primary factors contributing to this imbalance is the high cost of real estate, especially in urban centers where multiplexes are typically located. The exorbitant prices make it economically unviable for cinema operators to establish new theatres in smaller towns and cities. As a result, the expansion of multiplex chains has been concentrated in areas with favorable infrastructure and consumer demand, leaving other regions underserved.
Moreover, audience preferences and viewing habits vary significantly across different parts of the country. While metropolitan cities may have a diverse audience that appreciates a wide range of film genres and languages, smaller towns and rural areas often have more limited tastes. This disparity in preferences influences the type of content that filmmakers produce and the distribution strategies adopted by distributors and exhibitors.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on catering to the preferences of urban audiences, particularly those in metropolitan areas. Films targeting the multiplex-going demographic, featuring niche genres and unconventional storytelling, have gained prominence. However, this trend has also led to a neglect of audiences in non-metro regions, where traditional, mainstream cinema continues to dominate. To address these challenges and promote inclusive growth, industry stakeholders must adopt a holistic approach that takes into account the diverse needs and aspirations of audiences across the country.
This includes exploring innovative business models, leveraging technology to enhance the cinematic experience, and investing in infrastructure development in underserved regions. Additionally, government intervention and policy support are crucial in facilitating the expansion of the cinema industry and ensuring equitable access to entertainment opportunities. Incentives for multiplex operators to establish theatres in non-metro areas, subsidies for the development of cinema infrastructure, and initiatives to promote regional cinema can help bridge the gap and foster a more inclusive film ecosystem.
Ultimately, the growth of India’s cinema industry hinges on its ability to embrace diversity, adapt to evolving consumer preferences, and overcome geographical and socioeconomic barriers. By addressing these challenges collectively and collaboratively, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of the country’s rich cinematic heritage and drive sustainable growth for the future.


 Opinion2 years ago
Opinion2 years ago
 Fashion7 years ago
Fashion7 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago
 Opinion2 years ago
Opinion2 years ago
 Business News2 years ago
Business News2 years ago
 Policy&Politics2 years ago
Policy&Politics2 years ago
 Business News2 years ago
Business News2 years ago