Economic
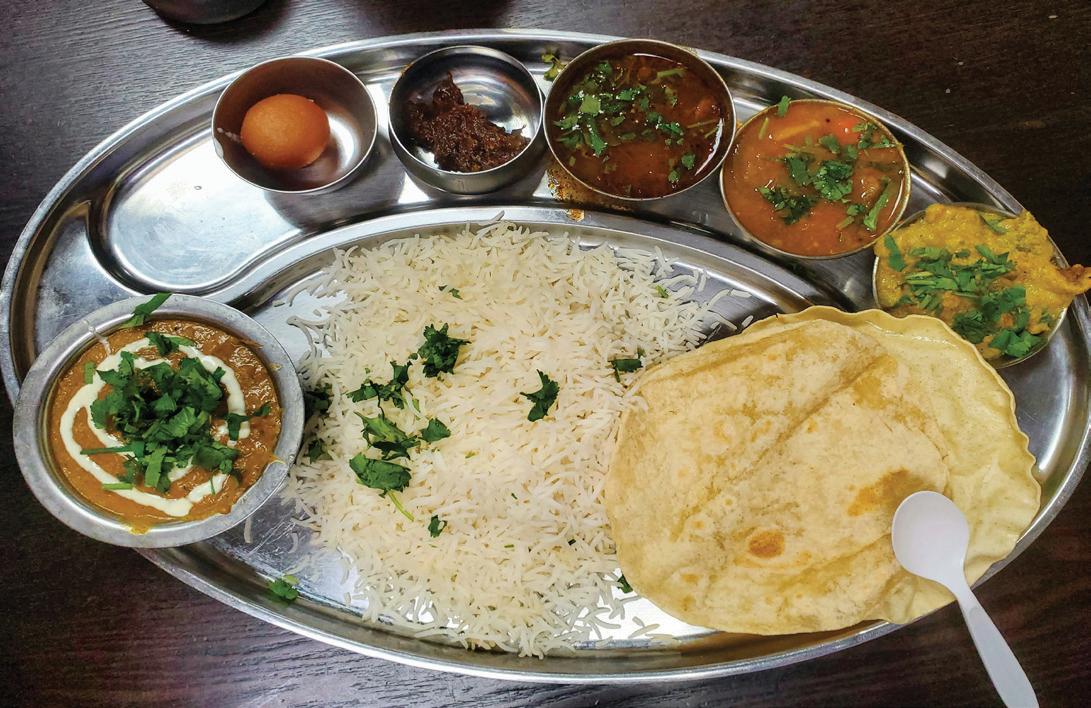
Veggie thali costs more, non-veg thali now more affordable

The Daily Guardian is now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@thedailyguardian) and stay updated with the latest headlines.
For the latest news Download The Daily Guardian App.
International Relations
UN raises India’s 2024 growth forecast to nearly 7%
International Relations
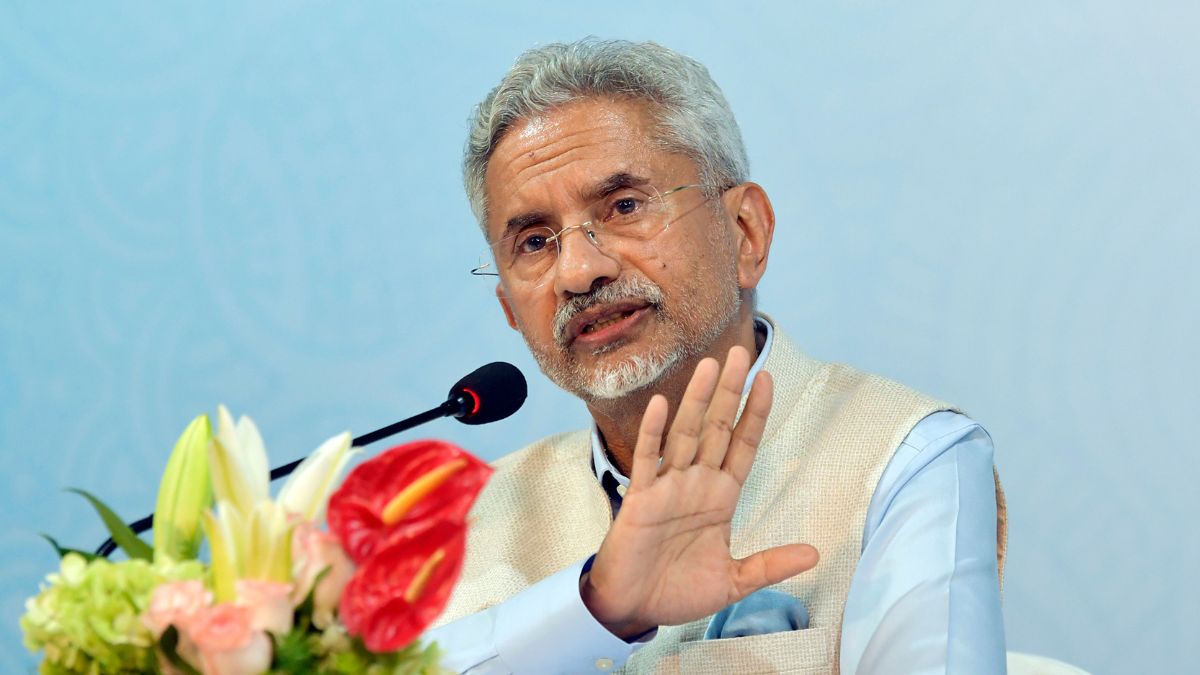
Jaishankar seeks ‘more than business-as-usual’ to tackle global challenges
Economic
India needs its own global giants like JP Morgan and Citibank, says Niti Aayog CEO
Economic
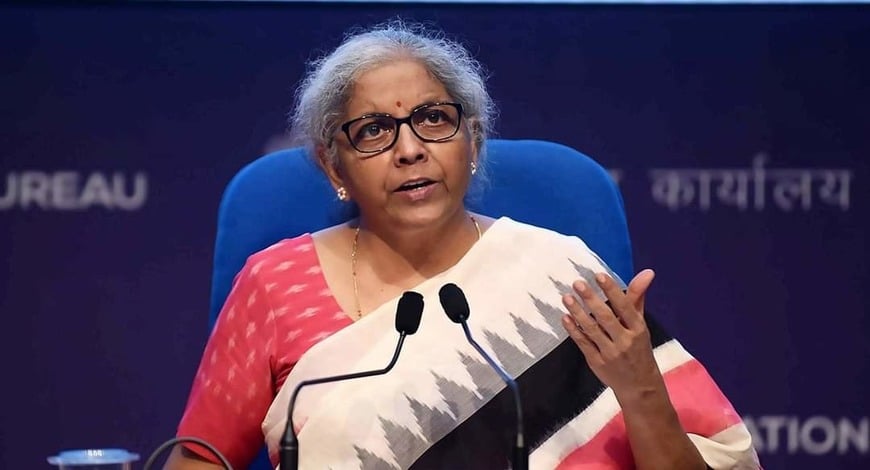
Sitharaman calls for proactive govt-industry alliances towards developed India
Economic
Rupee112 aims for Rs1000 cr revenue, 3L loans by FY2027
Economic
India’s PE-VC market sees mixed results in challenging year
-

 Opinion3 years ago
Opinion3 years agoPakistan-China nexus trying to sow doubts in Indian society about governance systems
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Fashion8 years ago
Fashion8 years agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Opinion3 years ago
Opinion3 years agoEnvironment day with a missing spring and lost souls
-

 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years agoIllinois’ financial crisis could bring the state to a halt
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoNew Season 8 Walking Dead trailer flashes forward in time
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoMod turns ‘Counter-Strike’ into a ‘Tekken’ clone with fighting chickens